Sun in H-Alpha - 2012 Aug 05 - 2
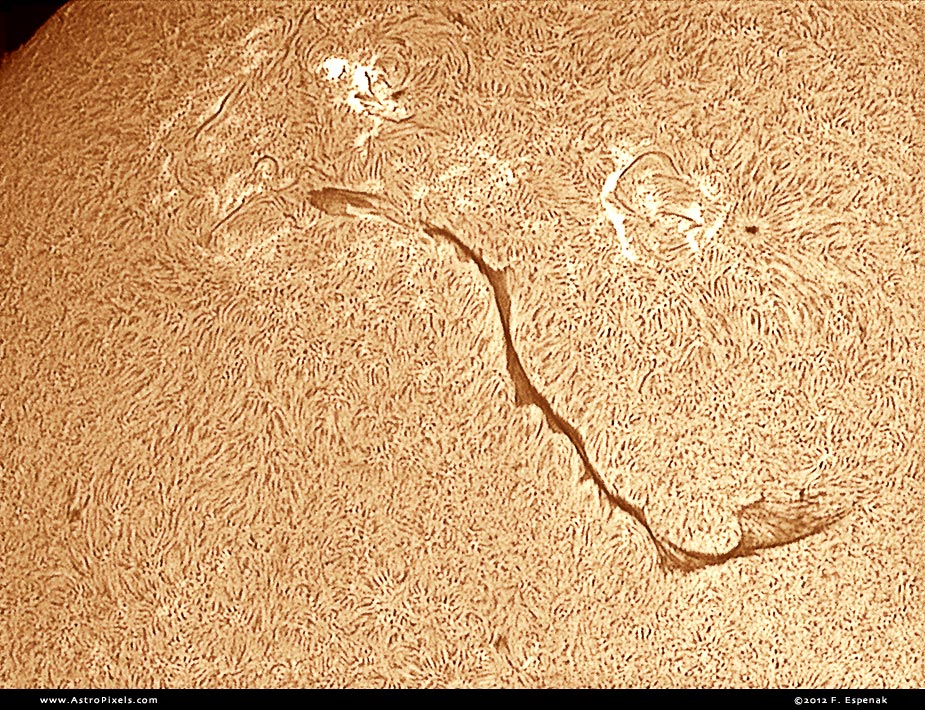
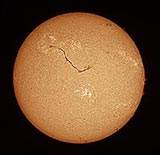
In early August, an enormous filament was seen stretching across the Sun's disk. This image through a hydrogen-alpha filter reveals the filament which is actually a prominence seen in front of the Suns surface. The image is oriented with Celestial North up.
H-alpha is a narrow line at the red end of the visible spectrum. It is caused by a transition in the hydrogen atom when an electron drops from its third to second lowest energy level.
The Sun is composed primarily of hydrogen and its upper atmosphere or chromosphere glows in the red light of h-alpha. A telescope with a specially designed h-alpha filter can reveal amazing structures in the chromosphere that are not visible in white light. Enormous prominences rise above the Sun's surface reaching altitudes of 150,000 km or more. When seen silhouetted against the solar disk prominences are then called filaments. They often underlie coronal mass ejections and are important to the prediction of space weather. Spicules are long thin tubes of luminous gas that can change in a matter of minutes. Powerful magnetic explosions known as solar flares form in the most active regions and eject clouds of electrons, ions, and atoms through the Sun's corona into space.
Technical Details
- Object: Sun in H-Alpha - 2012 Aug 05 - 2
- Date/Time: 2012 Aug 05 at 18:49 UTC
- Location: Bifrost Astronomical Observatory, Portal, AZ
- Mount: Losmandy G-11 German Equatorial Mount
- Telescope: Coronado SolarMax 40 + Televue Powermate 2.5x
- Camera: Point Grey Research Chameleon (monochrome, 1.2 MP)
- Video Sequence: video composite at 15 fps, duration 18 seconds (270 frames)
- File Name: sunha12aug05-02w.jpg
- Data Acquisition: Dell 10v, PGR FlyCapture software
- Processing (Registax): stack 80% best images; wavelets
- Processing (Photoshop CS6): Layers, Masks, High Pass Filter, Curves, Color Balance
- Rights: Copyright 2012 by Fred Espenak. All Rights Reserved. See: Image Licensing.