Diffuse Nebulae Photo Gallery
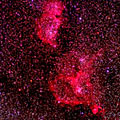
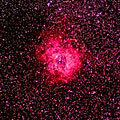
A diffuse nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust and gas. The gas consists mostly of hydrogen and helium, but other ionized gasses may be present. Diffuse Nebulae are often associated with star forming regions. The force of gravity collapses the cloud into clumps and knots where densities can grow high enough to initiate nuclear fusion in the cores of new stars. Some of the remaining dust and gas are believed to form planets and solar systems. Newly formed open clusters are also sometimes found still embedded within diffuse nebulae.
Diffuse Nebulae (sometimes called Bright Nebulae) generally cover extended areas and have no well-defined boundaries. They may be sub-divided into either reflection or emission. Reflection nebulae shine by light reflected from nearby stars. In contrast, emission nebulae contain ionized gasses that glow at specific spectral frequencies characteristic of the elements contained within. Ionized hydrogen dominates in many emission nebulae which are referred to as HII regions. They are easily recognized by the red glow due to hydrogen's strongest spectral line.
Dark nebulae do not emit or reflect light. Rather, they are seen in silhouette against a brighter background of stars or diffuse nebulae.
The 18th-century French astronomer Charles Messier recorded 7 diffuse nebulae in his Messier Catalog of deep sky objects. For more information, see the Wikipedia entry about nebulae.
Click on each thumbnail to see a larger image.